There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
By Sabyasachi (SK)
In Part 3 of this series, we explored how thousands of GPUs collaborate during training — dividing the work, computing millions of iterative waves, and synchronizing constantly through all-to-all communication.Now, we enter the next big challenge:👉 If GPUs are the engines of AI, the network is the bloodstream.
👉 And without the right network, AI training slows to a crawl.This chapter dives into what happens when all devices in the GPU cluster start talking to each other at the same time, and why the datacenter fabric becomes the most critical element of modern AI infrastructure.
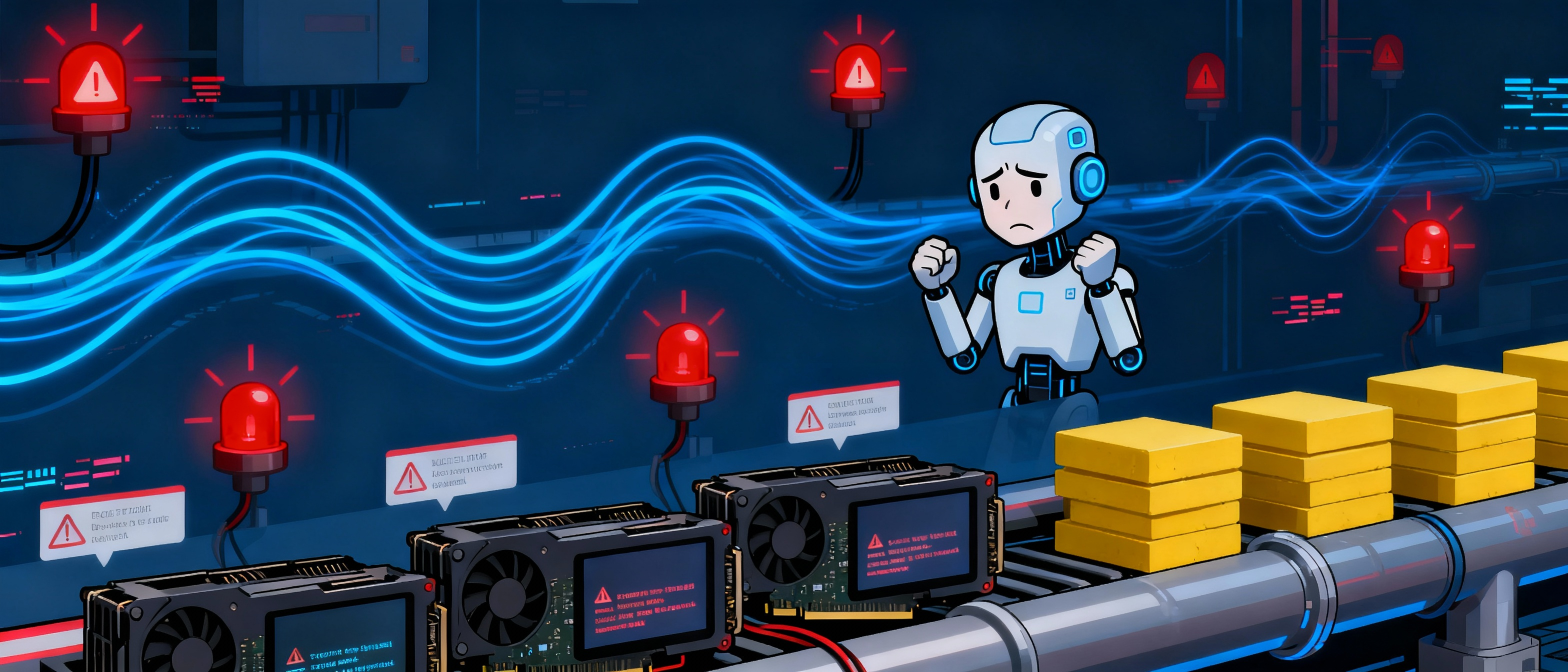
1. GPU-to-GPU Communication: Calm… Then Chaos
During LLM training, communication between GPUs is not constant — it’s bursty.Here’s what it looks like:
This is the heartbeat of AI training.

2. Why These Bursty Traffic Patterns Are Dangerous When all GPUs exchange information:
❌ Training slows
❌ GPU time is wasted
❌ Synchronization barriers take longer
❌ The entire training job stretches from months… to even more months
In short:
👉 If the network fails, the model fails.
👉 The network becomes the bottleneck.
3. The Most Important Moment in AI Networking
There is one critical event in AI training:⭐ The All-Gather / All-Reduce OperationThis is when:

Traditional datacenter networks (built for web, microservices, VMs, or storage) have traffic that looks like:
✔ High throughput
✔ Predictable latency
✔ Congestion avoidance
✔ Fair scheduling
✔ Fast recovery
✔ Zero packet drops (lossless fabrics)
✔ Multi-path routing optimized for parallel GPU workloads
This is why AI networks are engineered very differently.
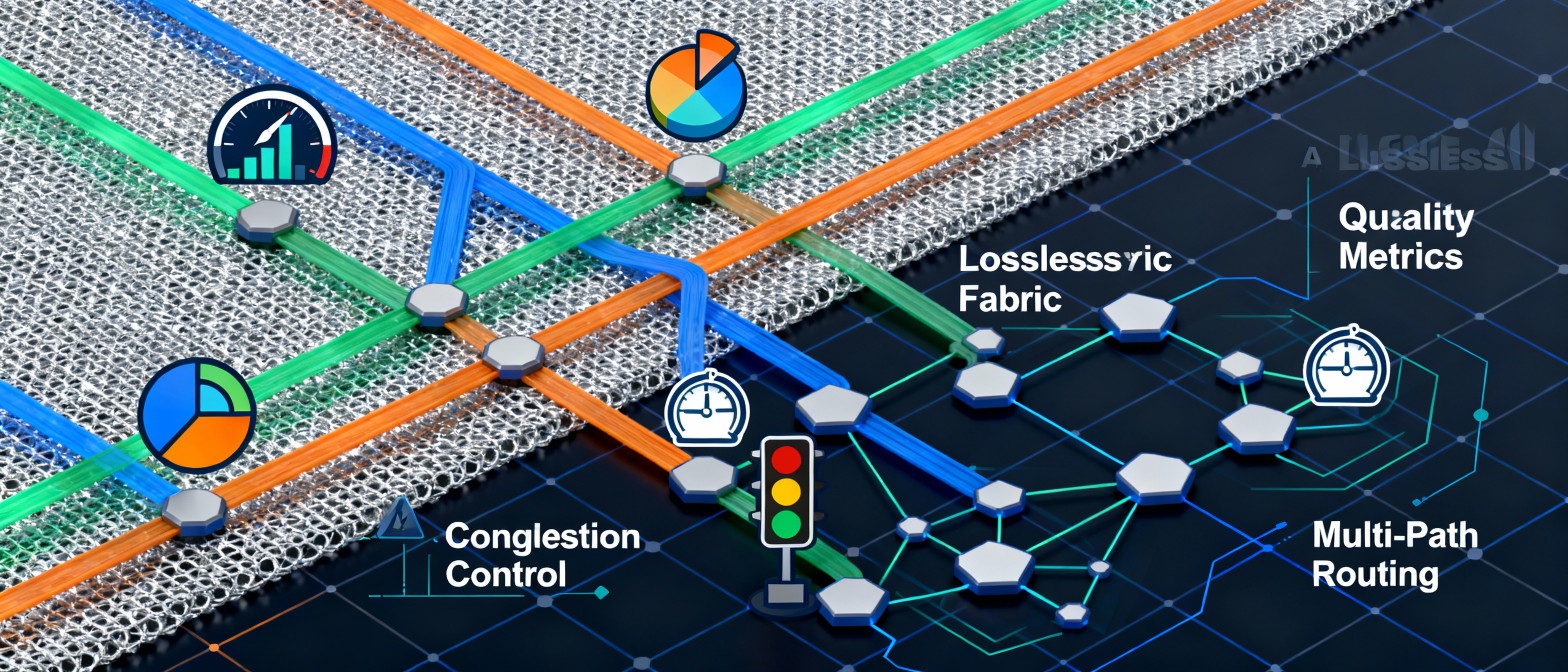
5. Traffic Engineering Becomes the Hero
AI networks depend heavily on:
1. Congestion ControlTo prevent queues from overflowing during GPU bursts.
Examples:
To distribute flows evenly across all available network paths.Examples:
These fabrics ensure:
✔ No single link gets overloaded
✔ All GPUs get equal bandwidth
✔ Bursty traffic doesn’t collapse the fabric
✔ Synchronization waves finish quickly
Without these, GPU clusters become inefficient and training slows dramatically.
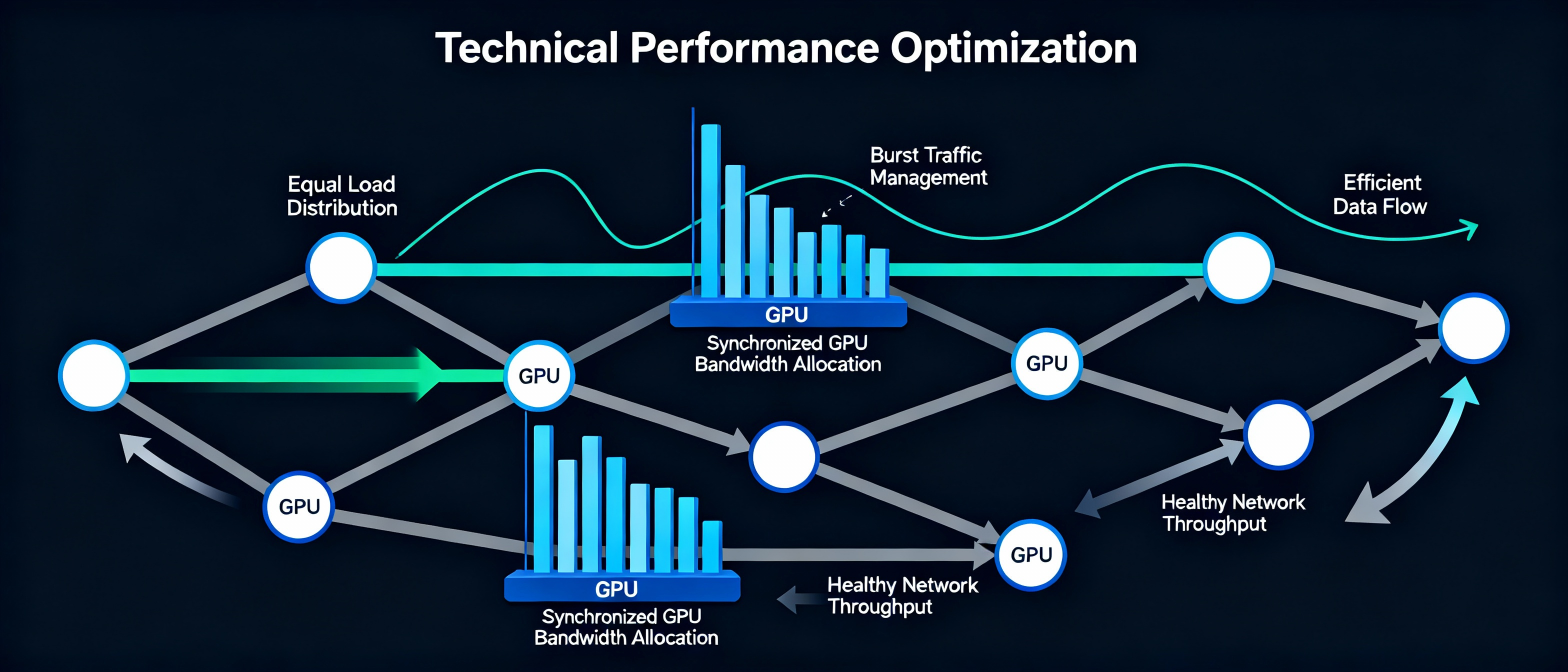
6. The Cost of Poor Networking
Let’s say your GPUs complete their computations in 200 microseconds…
but your network takes 2 milliseconds to synchronize.
Suddenly:
⚡ A fast training run and🐢 A year-long struggle

7. What Part 5 Will Cover Now that we understand:
Sabyasachi
Network Engineer at Google | 3x CCIE (SP | DC | ENT) | JNCIE-SP | SRA Certified | Automated Network Solutions | AI / ML (Designing AI DC)